Technical Articles
Useful Information
Is it better to change the brake pads and brake discs at the same time?
This is one of the most frequently asked questions. The answer is YES.
For example, the brake discs do not need to be changed if the car is relatively new and there is still a lot of disc life left. They absolutely need to be changed if the discs are unevenly worn or badly scored.
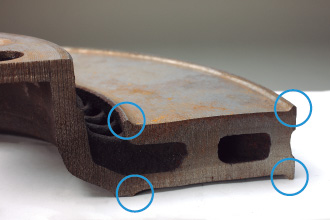
Take a look at the braking surface of the discs. There are ridges on the edges of the braking surfaces. The following is a simple illustration.

The points that are circled in RED are only points that the brake pad is in contact with the braking surface of the brake disc. If the brakes are in this condition, the braking power is obviously reduced, and it can even cause brake noise.
Braking force is created by the brake pad and brake disc. If one of the two are not in optimal condition, the actual braking potential cannot be achieved.
■ Brand new brake disc

■ Brake discs that need replacement


Brake discs in bad condition can not only cause decreased brake performance but also cause brake noise. DIXCEL recommends changing your discs and pads at the same time.
It is dangerous to drive with over-worn brake discs!
Have you ever thought, “Brake discs do not need to be changed because they are metal, and only the brake pads need replacement.” or, “I don’t drive on a race circuit and I drive safely on the street only so I don’t need it.”
Have you ever taken a look at your brake discs?
Either when the disc surface has circular scores like record discs, or cracks start to appear, people think it is time to replace it. In fact, even if the brake disc surface wears smoothly, when the outer edge has ridges, the brake disc is due for replacements.
Why do brake discs need replacement? The main reasons are ‘friction heat’, and ‘heat capacity’.
What is braking?
When you step on a brake pedal, the brake pads clamp against the brake discs to create friction.
By converting the friction energy to heat energy, the car is able to safely slow down.
This is how braking works. The ‘friction heat’ that occurs in the process is important.
Relation between Brake disc / pad
There is an amount of heat which brake disc / pad can store (so-called heat capacity).
If the new disc / pad heat capacity is “100”, as the wear of disc / pad progress, its heat capacity will be “90” → “80” →”70″ … and so on.
Then, the heat that cannot be stored by brake disc / pad will be transferred to the caliper or brake fluid to create various heat damages.
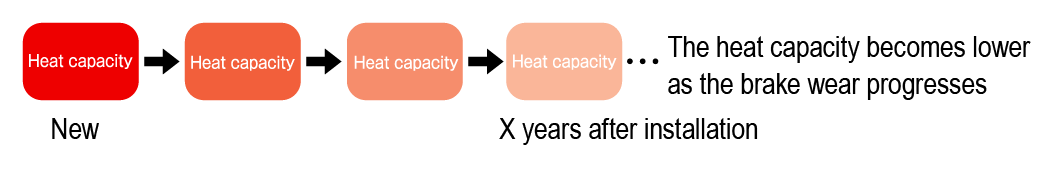
Heat damages are
The following examples are typical heat damages.
- Decreased rigidity of brake calipers
- Premature wear of discs/pads
- Distorted, cracked, uneven wear on discs
- Brake fluid vapor lock, fluid leakage from screws
- Friction material separation by bent brake pad back plates
To avoid the heat damage as much as possible, the regular condition check of discs/pads is very important.
Please use “Brake Temperature Indicator Stickers” to easily measures the peak temperature of the brake caliper for proper temperature management.
When do brake discs need replacement?

For the front disc, it is due for replacement when either side of the braking surface is worn more than 1mm. For the rear disc, when either side of the braking surface is worn by more than 0.5mm~0.75mm.
The Minimum thickness is stamped on each disc as “MIN TH OO” (The wear limit varies depending on part numbers).
With DIXCEL SD discs, slots are machined with a depth of approx.0.75mm. Therefore, it can be said that when slots start to disappear it is a sign that replacement is needed in the near future.
It is very dangerous to continue using over-worn brake discs. Please check the condition of your vehicle’s brake discs regularly.

